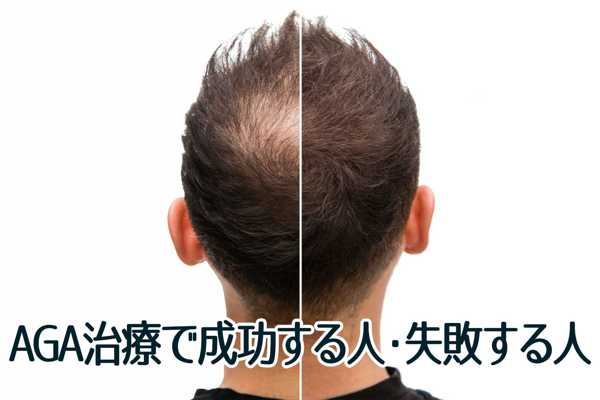
AGA治療とは?費用・治療法・クリニック選びまで徹底解説
Early Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer: A Guide to Timely Detection and Treatment
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, but thanks to advances in early detection and treatment, survival rates have significantly improved. The key to successful treatment lies in identifying the disease in its earliest stages. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of breast cancer can make a life-saving difference. This article will guide you through the common symptoms, the importance of early detection, and the latest treatment options available.
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, but thanks to advances in early detection and treatment, survival rates have significantly improved. The key to successful treatment lies in identifying the disease in its earliest stages. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of breast cancer can make a life-saving difference. This article will guide you through the common symptoms, the importance of early detection, and the latest treatment options available.

What is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer occurs when cells in the breast begin to grow abnormally, forming a mass or tumor. These cancerous cells can also spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early. With timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for breast cancer can be greatly improved, emphasizing the importance of awareness and early detection.
Common Early Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer
Not all breast cancer cases present with obvious symptoms, but many early signs can be noticeable. Regular self-exams, along with mammograms and clinical exams, are essential for early detection. Below are the most common symptoms to watch out for:
1. A New Lump in the Breast
The most common and noticeable symptom of breast cancer is a lump or mass in the breast. This lump may be hard, irregular in shape, and may not cause pain. While many lumps are benign, any new or unexplained lump should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional.
2. Changes in Breast Shape or Size
Unexpected changes in the size or shape of the breast can signal potential issues. This may include one breast appearing larger than the other or experiencing a sudden change in shape. Such changes may result from a developing tumor, which can alter the breast's normal contours.
3. Skin Changes
Changes to the skin on the breast can be an important indicator of breast cancer. These changes can include:
- Dimping: The skin of the breast may deveop a texture resembing an orange pee (aso known as peau d'orange).
- Redness or Irritation: The skin of the breast may become red, infamed, or itchy.
- Thickening or Sweing: The skin may fee thickened or swoen in certain areas, which can be a sign of cancer affecting the underying tissue.
4. Nipple Changes
Changes in the appearance of the nipple can be a red flag. These may include:
- Inversion: The nippe turning inward, a symptom of potentia underying cancer.
- Pain or Tenderness: Persistent pain or tenderness in the nippe or breast.
- Redness, Scaing, or Itching: The skin around the nippe may become irritated, faky, or scay.
5. Nipple Discharge (Other Than Breast Milk)
Any discharge from the nipple that is not breast milk, especially if it is clear or bloody, should be investigated by a healthcare provider. This could be a sign of an infection or, in some cases, breast cancer.
6. Persistent Pain or Tenderness
While most breast pain is not due to cancer, any persistent or severe pain should be evaluated. Pain that doesn’t correspond with your menstrual cycle or lasts for weeks may warrant further investigation, especially if it’s localized to a specific area of the breast.
7. Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes under the arm or near the collarbone can indicate that cancer cells have spread to the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes are often the first place where cancer spreads outside the breast, so enlargement in these areas should not be ignored.
Why Early Detection is Crucial
The earlier breast cancer is detected, the better the chances of successful treatment. Early-stage breast cancer often responds well to treatment and has a higher survival rate. Regular mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-exams are vital for detecting cancer in its early stages, even before symptoms appear. Mammograms are particularly important for women over 40, but those with a family history or genetic risk may need to begin screenings earlier.
Modern Treatment Options for Breast Cancer
Once diagnosed, breast cancer treatment options vary depending on the cancer's stage, type, and the patient's health. The primary treatment options include:
1. Surgery
Surgery is often the first treatment for early-stage breast cancer and may involve removing the tumor (lumpectomy) or the entire breast (mastectomy). In some cases, lymph nodes may also be removed to check if the cancer has spread.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It is typically used in cases where cancer has spread beyond the breast or for larger tumors. Chemotherapy may also be used after surgery to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
3. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells in the breast and surrounding tissue. It is often used after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of the cancer returning.
4. Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is used to block the hormones (estrogen and progesterone) that fuel certain types of breast cancer. It can be used in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer to reduce the risk of recurrence or to shrink tumors before surgery.
5. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies are drugs designed to target specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer. For example, drugs like Trastuzumab (Herceptin) are used to target HER2-positive breast cancers, which are more aggressive.
6. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to help fight cancer cells. While still a relatively new approach, immunotherapy is showing promise, especially for triple-negative breast cancer, which lacks receptors for estrogen, progesterone, and HER2.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent breast cancer, certain lifestyle choices can reduce the risk:
- Exercise Reguary: Physica activity can hep maintain a heathy weight and reguate hormones, both of which can ower breast cancer risk.
- Heathy Diet: A baanced diet rich in fruits, vegetabes, and whoe grains can hep reduce cancer risk. Limiting processed foods and red meats may aso contribute to better overa heath.
- Limit Acoho Consumption: Studies show a ink between acoho consumption and an increased risk of breast cancer. Limiting intake can reduce this risk.
- Breastfeed if Possibe: Breastfeeding for severa months can ower the risk of breast cancer.
- Know Your Famiy History: Genetic factors pay a roe in breast cancer risk. Women with a famiy history of the disease shoud discuss genetic testing and screening with their doctor.
Advancements in Breast Cancer Treatment
With ongoing research, new treatments are continually improving the outlook for breast cancer patients. Precision medicine, which tailors treatment to an individual’s genetic makeup, is becoming increasingly important. This personalized approach ensures that patients receive the most effective therapies with fewer side effects. Additionally, research into immunotherapy and targeted therapies offers hope for more effective treatments in the future.
Conclusion
Breast cancer is a serious disease, but early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and recovery. By being aware of the early signs and symptoms, performing regular self-exams, and scheduling routine screenings, you can increase your chances of detecting breast cancer early. If you notice any of the warning signs mentioned above, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional immediately. Early diagnosis, along with advancements in treatment, means that many women diagnosed with breast cancer today can live long, healthy lives. Stay vigilant, be proactive about your health, and never hesitate to seek medical advice if you have concerns.