東京での離婚相談なら信頼できる弁護士にお任せ
Understanding HIV-Related Rashes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including skin rashes. These rashes are common in people living with HIV and can be a key indicator of the disease. Here’s what you need to know about HIV-related rashes.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including skin rashes. These rashes are common in people living with HIV and can be a key indicator of the disease. Here’s what you need to know about HIV-related rashes.
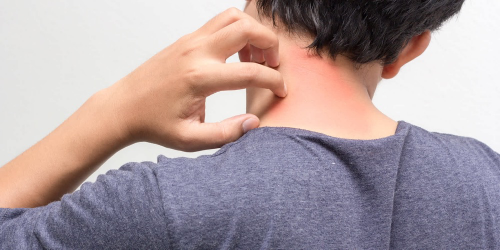
What is an HIV Rash?
An HIV rash is a common symptom, particularly in the early stages of the infection. It usually appears within two months of contracting HIV, with typical locations being the hands, legs, face, and chest. The rash often manifests as red spots or bumps, and it is accompanied by persistent itching.
What Causes HIV Rash?
The cause of an HIV rash can vary. In some cases, the rash appears as a direct symptom of the HIV infection. In others, it may be triggered by medications used to treat the disease, particularly antiretroviral drugs. However, the exact cause is often difficult to pinpoint.
What Makes the Rash Worse?
Several factors can aggravate an HIV rash, including:
- Infections or Allergies:Other infections or allergic reactions can worsen the rash.
- Medications:Certain medications can make the rash more severe.
- Sun Exposure:Direct sunlight can exacerbate the condition.
- Diet Changes:Sudden changes in diet or eating habits.
- Skin Products:Switching toiletries frequently can irritate the skin.
- Extreme Temperatures:Hot showers or extreme temperatures can also worsen symptoms.
Seroconversion Rash
Shortly after contracting HIV, many people develop a rash known as seroconversion rash. This rash is a sign that the body is starting to produce HIV antibodies. It is usually flat, red, and located on the chest or back. Unlike other HIV rashes, seroconversion rashes typically do not cause itching.
Cellulitis: A Serious Skin Infection
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that often affects HIV-positive individuals. This infection causes redness, swelling, and intense pain in the skin. In severe cases, fever and red streaks extending from the infection site may appear. Immediate medical attention is essential for treating cellulitis.
Herpes and HIV
People living with HIV are more prone to severe outbreaks of herpes. Herpes simplex (types 1 and 2) causes painful blisters, often in the mouth or genital area. Herpes zoster (shingles), a related infection, can affect one or both sides of the body and is common among those with weakened immune systems.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that causes a red, circular rash. HIV-positive individuals are particularly vulnerable to fungal infections like ringworm, which can spread quickly if left untreated.
Managing HIV-Related Rashes
If you notice any rash-like symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Treatment for rashes may involve:
- Topical Treatments:Corticosteroids or anti-fungal creams can help reduce irritation.
- Antibiotics:For bacterial infections like cellulitis, oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Herpes Treatment:Antiviral medications can help manage herpes outbreaks and prevent complications.
Conclusion
HIV-related rashes are common but can be managed effectively with the right treatment. Early diagnosis and appropriate care are essential for alleviating discomfort and preventing further complications. If you’re living with HIV and notice any skin changes, be sure to seek medical advice to ensure proper care and treatment.











