太陽光パネル設置工事の仕事を探している求職者のためのガイド
Advances in Asthma Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Symptoms Effectively
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of individuals globally, is characterized by airway inflammation and narrowing, making breathing difficult. While there is no cure for asthma, significant advancements in treatment options have made it more manageable than ever. This article explores the latest developments in asthma treatment, focusing on key strategies such as inflammation control, biologic therapies, and lifestyle modifications that empower patients to live healthier lives.
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of individuals globally, is characterized by airway inflammation and narrowing, making breathing difficult. While there is no cure for asthma, significant advancements in treatment options have made it more manageable than ever. This article explores the latest developments in asthma treatment, focusing on key strategies such as inflammation control, biologic therapies, and lifestyle modifications that empower patients to live healthier lives.
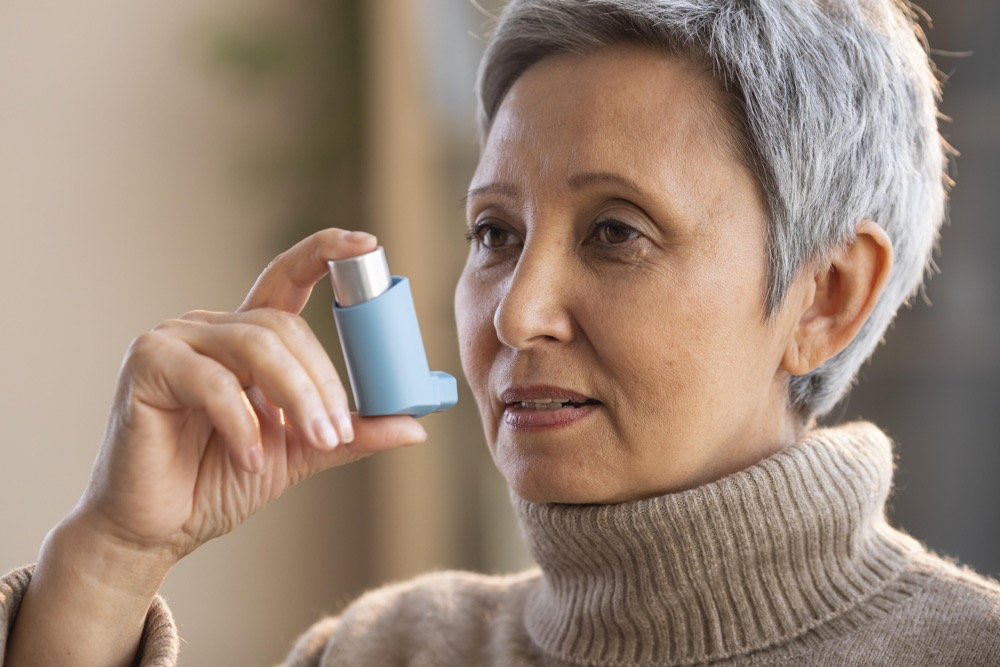

1. Inflammation Control as the Cornerstone of Asthma Management
In the past, asthma treatment often focused on relieving symptoms through quick-relief inhalers. However, recent treatment guidelines emphasize the importance of controlling the underlying inflammation that triggers asthma attacks. Long-term control medications, primarily inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), are now recommended as the first line of defense for managing asthma.
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS): ICS have long been recognized as the most effective medication for reducing airway inflammation. These medications are typically prescribed for daily use, even for patients with mild asthma, to prevent symptoms and minimize the need for rescue inhalers.
Combination Inhalers: New guidelines suggest combining ICS with Long-Acting Beta₂-Agonists (LABAs). This combination approach provides a dual benefit: ICS controls inflammation, while LABAs help maintain open airways, improving overall asthma control.
2. Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma
For individuals with severe asthma that doesn’t respond well to traditional treatments, biologic therapies offer a new avenue for treatment. These innovative medications target specific parts of the immune system involved in the inflammatory process, providing relief for patients with hard-to-control asthma.
Targeting IL-5 and IgE: Biologic drugs like mepolizumab (anti-IL-5) and omalizumab (anti-IgE) have been shown to be effective for patients with allergic asthma or eosinophilic asthma. These medications are typically reserved for severe cases and are administered through injections.
3. Reducing Reliance on Rescue Medications
One of the latest trends in asthma management is reducing the reliance on rescue inhalers. While these medications offer quick relief during an asthma attack, overuse can indicate poor asthma control and lead to more severe flare-ups.
Rescue Inhalers (SABAs): New treatment guidelines recommend that rescue inhalers be used sparingly and only during an asthma attack. Instead, a more consistent treatment plan focused on daily medications like ICS and combination inhalers should be prioritized.
4. Lifestyle and Environmental Control
Asthma management extends beyond medication, with a growing focus on lifestyle changes and environmental control. Minimizing exposure to asthma triggers such as allergens, smoke, and pollution can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
Allergen Avoidance: Measures like using air purifiers, reducing pet exposure, and keeping living spaces clean can help lower the presence of asthma triggers.
Exercise: While physical activity is beneficial for overall lung health, patients with exercise-induced asthma should take precautions. This may include using a rescue inhaler before engaging in physical activities.
5. The Role of Patient Education
Patient education is a vital component of effective asthma management. By empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, proper medication usage, and recognizing the signs of worsening symptoms, asthma control becomes a shared responsibility between healthcare providers and patients.
Personalized Asthma Action Plans: A tailored asthma action plan is a practical tool that helps patients manage their symptoms, decide when to adjust their medication, and know when to seek medical assistance.
Conclusion
Recent advances in asthma management emphasize a more comprehensive approach that addresses inflammation, improves long-term control, and offers individualized care. By incorporating medications, environmental control strategies, and patient education, individuals with asthma can experience a higher quality of life and better disease control. The focus on inflammation and biologic therapies for severe cases reflects the growing understanding of asthma as a complex condition that requires multifaceted management.