現在募集中:コミュニティ内の看護職を募集中です!
Effective Colitis Management: Treatment Options and Approaches
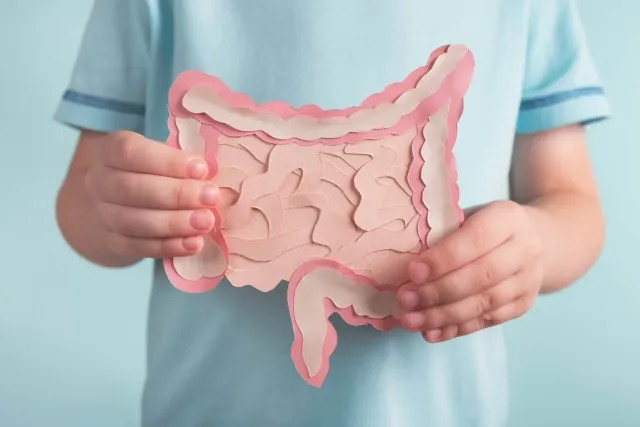
Colitis is an inflammatory condition that can significantly affect an individual’s gastrointestinal system, leading to symptoms such as pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. Proper management of colitis is essential for maintaining health and preventing complications. This article outlines the most effective treatments for colitis, including both conventional medical therapies and lifestyle adjustments.
Colitis is an inflammatory condition that can significantly affect an individual’s gastrointestinal system, leading to symptoms such as pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. Proper management of colitis is essential for maintaining health and preventing complications. This article outlines the most effective treatments for colitis, including both conventional medical therapies and lifestyle adjustments.
Conventional Medical Treatments for Colitis
Treatment for colitis generally begins with medication aimed at reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the individual’s response to previous therapies.
1. Aminosalicylates (5-ASA)
These drugs are used to treat mild to moderate colitis. They help reduce inflammation in the colon and maintain remission.
• Common examples: Mesalamine, Sulfasalazine
• Benefits: Safe and effective for many patients
• Side effects: Rare, but may include nausea or headache
2. Steroids
For patients with more severe symptoms, corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation quickly. However, they are typically only used for short-term treatment due to side effects with prolonged use.
• Common examples: Prednisone, Budesonide
• Benefits: Quick relief from severe flare-ups
• Side effects: Weight gain, osteoporosis, mood changes with long-term use
3. Immunosuppressive Drugs
These medications suppress the immune system to prevent it from attacking the colon. They are used for long-term maintenance to reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
• Common examples: Azathioprine, Methotrexate
• Benefits: Helps maintain remission and reduce flare-up frequency
• Side effects: Increased risk of infections, liver problems
4. Biologic Drugs
Biologic therapies are a newer class of drugs that target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process. These are typically used for moderate to severe colitis cases.
• Common examples: Infliximab, Adalimumab
• Benefits: Effective for hard-to-treat cases of colitis
• Side effects: Risk of infection, allergic reactions
5. Antibiotics
If bacterial infections are a concern, antibiotics may be used to prevent or treat infections that could worsen colitis symptoms.
• Common examples: Metronidazole, Ciprofloxacin
• Benefits: Treats bacterial infections, improving symptoms
• Side effects: Diarrhea, nausea
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
While medications are an essential part of treatment, diet and lifestyle play a vital role in managing colitis and improving long-term outcomes.
1. Identifying Trigger Foods
Certain foods may exacerbate symptoms of colitis. These include high-fiber foods, dairy, spicy foods, and caffeine. Avoiding these can help reduce flare-ups.
2. Small, Frequent Meals
Eating smaller, more frequent meals is easier on the digestive system and helps reduce discomfort.
3. Adequate Hydration
Drinking enough water is crucial, especially during flare-ups, to replace fluids lost through diarrhea and prevent dehydration.
4. Stress Reduction
Since stress can worsen colitis symptoms, stress management techniques such as yoga, mindfulness, and deep breathing exercises are essential.
5. Physical Activity
Regular exercise can help reduce stress and promote overall digestive health. It also helps maintain a healthy weight, which is important for managing colitis.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where medication and lifestyle changes do not control symptoms, surgery may be necessary.
1. Colectomy
Colectomy involves the removal of part or all of the colon. If the entire colon is removed, a patient may require an ileostomy, where waste is diverted to an external bag.
2. Strictureplasty
This surgical option involves widening narrowed parts of the colon to improve bowel function and alleviate symptoms.
3. Resection
Resection involves removing only the affected portion of the colon, preserving as much healthy tissue as possible.
Complementary Therapies
Some patients find additional relief through complementary therapies, which can be used alongside conventional treatments.
1. Probiotics
Probiotics can help balance gut bacteria, improving digestion and reducing inflammation.
2. Herbal Remedies
Herbs like aloe vera and turmeric have anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate colitis symptoms.
3. Acupuncture
Acupuncture may offer relief from pain and inflammation, though more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.
Conclusion
Colitis is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted treatment approach. With a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery, individuals with colitis can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can make the best decisions for their health and well-being.