借金減額診断で見直す負担軽減の第一歩
Managing Colitis: A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment Options
Colitis, which refers to inflammation of the large intestine, can significantly impact a person's daily life. The condition is often associated with painful symptoms like abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and fatigue. Effective management of colitis is key to maintaining a good quality of life and preventing long-term complications. This article explores the treatment options for colitis, including medications, lifestyle changes, surgical interventions, and complementary therapies.
Colitis, which refers to inflammation of the large intestine, can significantly impact a person's daily life. The condition is often associated with painful symptoms like abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and fatigue. Effective management of colitis is key to maintaining a good quality of life and preventing long-term complications. This article explores the treatment options for colitis, including medications, lifestyle changes, surgical interventions, and complementary therapies.
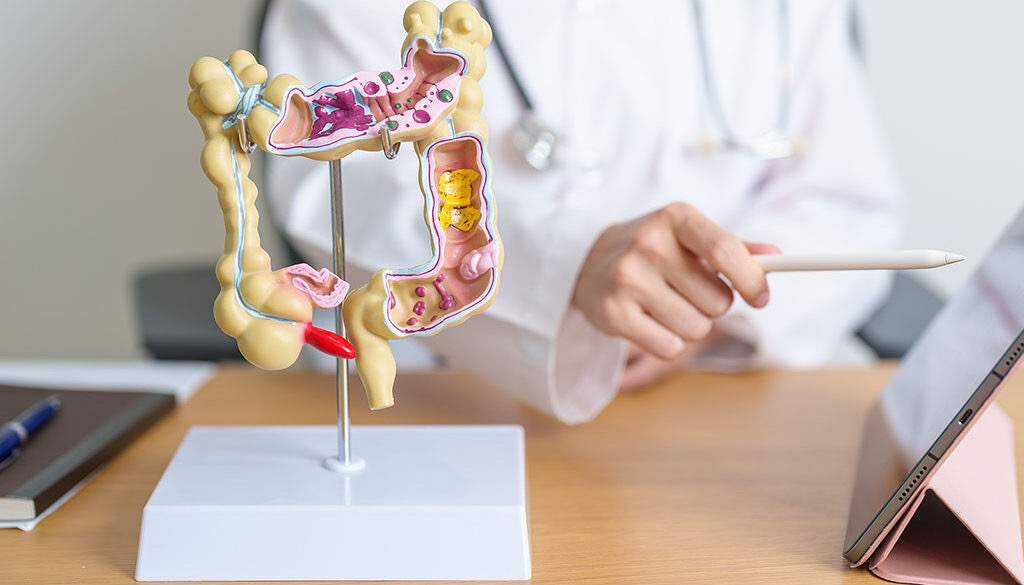
Medical Treatments for Colitis
A variety of medications are used to treat colitis, depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause of inflammation.
1. Aminosalicylates (5-ASA)
These anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly prescribed for mild to moderate colitis. They are designed to reduce inflammation directly in the colon, helping to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
• Common examples: Mesalamine, Sulfasalazine
• Benefits: Well-tolerated and effective for treating inflammation
• Side effects: Possible mild nausea or headache
2. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are used to treat more severe inflammation in colitis. While they are highly effective in reducing symptoms, they are typically used for short periods due to potential long-term side effects.
• Common examples: Prednisone, Hydrocortisone
• Benefits: Rapid symptom relief, effective for acute flare-ups
• Side effects: Weight gain, increased blood sugar, osteoporosis with long-term use
3. Immunosuppressants
These drugs suppress the immune system’s response to reduce inflammation in colitis patients who don’t respond well to other treatments. They are commonly used for long-term maintenance.
• Common examples: Azathioprine, Methotrexate
• Benefits: Prevents flare-ups and maintains remission
• Side effects: Risk of infections, liver damage, or bone marrow suppression
4. Biologic Agents
Biologics target specific immune system proteins that contribute to inflammation. These treatments are often prescribed for moderate to severe colitis that does not respond to conventional drugs.
• Common examples: Infliximab, Adalimumab
• Benefits: Highly effective for difficult-to-treat cases
• Side effects: Increased risk of infections and infusion reactions
5. Antibiotics
In some cases, bacterial infections may worsen colitis symptoms. Antibiotics may be used to treat these infections and improve symptoms.
• Common examples: Metronidazole, Ciprofloxacin
• Benefits: Clears bacterial infections and alleviates related symptoms
• Side effects: Nausea, upset stomach
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medications, managing diet and lifestyle is an essential part of colitis treatment.
1. Avoiding Trigger Foods
Certain foods can trigger flare-ups in colitis patients. Common culprits include spicy foods, dairy products, high-fiber foods, and caffeinated drinks. Identifying and avoiding these foods can help reduce symptoms.
2. Small, Frequent Meals
Eating smaller, more frequent meals rather than large meals can ease digestion and reduce the strain on the gastrointestinal system.
3. Hydration
Colitis can lead to dehydration, especially during flare-ups due to diarrhea. Drinking plenty of fluids is essential for maintaining hydration and supporting overall health.
4. Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate colitis symptoms. Activities such as yoga, deep breathing exercises, and meditation can help manage stress and improve well-being.
5. Regular Exercise
Exercise helps reduce stress, improve circulation, and maintain a healthy weight, which can all contribute to better digestive health.
Surgical Options for Severe Colitis
For some patients, particularly those with severe or unresponsive colitis, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options aim to remove diseased parts of the colon and improve quality of life.
1. Colectomy
A colectomy involves the removal of part or all of the colon. In some cases, an ileostomy (a bag placed outside the body to collect waste) may be required.
2. Strictureplasty
This procedure is used to widen narrow portions of the colon caused by scarring. It can improve bowel function and relieve symptoms.
3. Resection
Resection involves removing the affected portion of the colon while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible. This option is usually recommended for localized disease.
Complementary Therapies
Some patients find relief through alternative therapies that complement conventional treatments.
1. Probiotics
Probiotics can help restore the balance of healthy bacteria in the gut, which may improve digestion and reduce inflammation.
2. Herbal Supplements
Herbs like turmeric and aloe vera have natural anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit those with colitis. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before using these supplements.
3. Acupuncture
Acupuncture may help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with colitis. Some studies suggest it can complement traditional treatments for better outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective treatment for colitis requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical therapies, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery. By collaborating with healthcare providers and exploring various treatment options, patients can better manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Understanding these treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their condition and make informed decisions about their care.