投資するなら今がチャンス!初心者でも安心の資産運用ガイド
New Approaches in Asthma Management: Guidelines and Treatment Shifts
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which leads to symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. While asthma cannot be completely cured, it can be effectively managed through medications, lifestyle changes, and ongoing patient education. Over time, there have been significant shifts in the guidelines and treatment strategies for asthma, making asthma management more personalized and effective. This article explores these evolving approaches and how they impact asthma care today.
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which leads to symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing. While asthma cannot be completely cured, it can be effectively managed through medications, lifestyle changes, and ongoing patient education. Over time, there have been significant shifts in the guidelines and treatment strategies for asthma, making asthma management more personalized and effective. This article explores these evolving approaches and how they impact asthma care today.
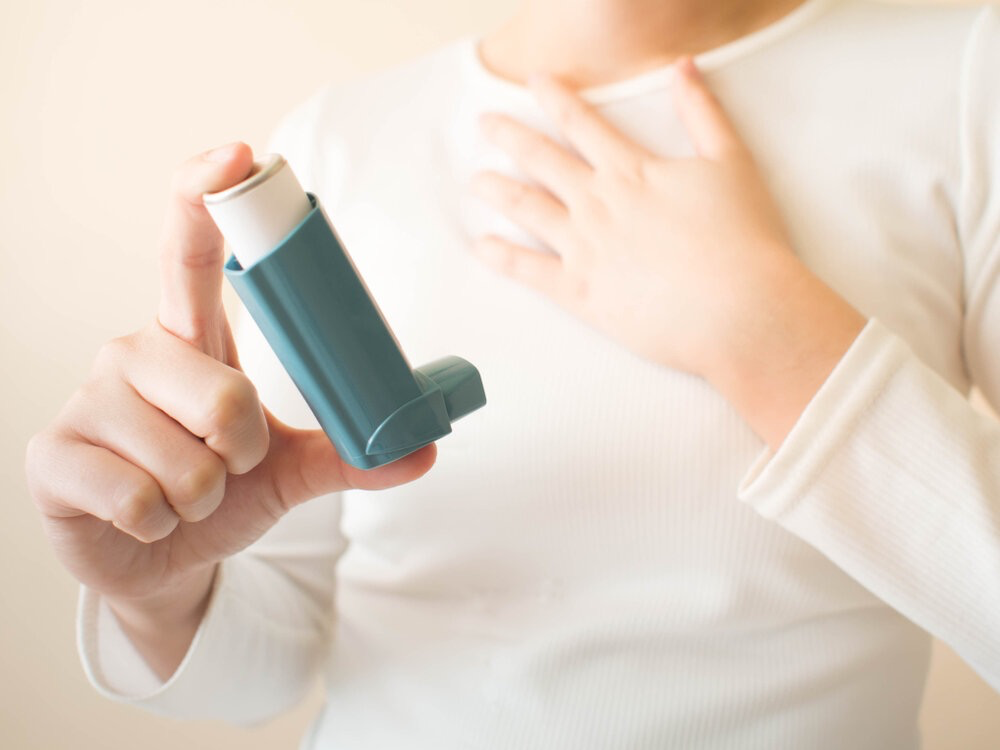

1. A Shift in Medication Focus: Inhalers and Anti-inflammatory Treatments
Recent guidelines have placed a greater emphasis on reducing the underlying inflammation in the airways rather than relying solely on short-term rescue inhalers for relief. This shift comes as studies have shown that over-relying on quick-relief medications, such as Short-Acting Beta₂-Adrenergic Agonists (SABAs), can lead to poorer asthma control and increased risk of exacerbations.
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS): ICS have remained a cornerstone in asthma treatment as they reduce airway inflammation and prevent asthma attacks. Recent recommendations highlight the importance of consistent ICS use for long-term control, even in cases of mild asthma. Regular use can reduce reliance on rescue medications and help maintain better overall lung function.
Combination Inhalers: Combining an ICS with a Long-Acting Beta₂-Adrenergic Agonist (LABA), such as salmeterol or formoterol, has proven to be highly effective. These medications help to reduce both airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction, offering better control over asthma symptoms.
2. Biologic Therapies for Severe Asthma
For patients with severe asthma that does not respond well to traditional treatments, biologic therapies have emerged as a promising option. These advanced medications target specific immune system components to reduce inflammation and prevent asthma attacks.
Monoclonal Antibodies: Drugs such as omalizumab (anti-IgE), mepolizumab (anti-IL-5), and dupilumab (anti-IL-4Rα) are designed for patients with severe asthma, particularly those who have high levels of eosinophils or allergic asthma. Biologics are typically administered via injection and are considered after other therapies have been exhausted.
3. Environmental Control: Reducing Triggers and Improving Quality of Life
Environmental control has become an essential part of asthma management. Reducing exposure to triggers such as allergens and irritants can prevent asthma flare-ups and improve overall health.
Allergen Avoidance: Common triggers include pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and mold. Maintaining a clean living space, using air purifiers, and avoiding pets in the bedroom are some strategies that can reduce allergen exposure.
Avoiding Air Pollution: Exposure to outdoor pollutants, such as tobacco smoke and car exhaust, can exacerbate asthma symptoms. Encouraging patients to avoid high-pollution areas or to wear masks when necessary can significantly reduce symptom severity.
4. Exercise and Lifestyle Modifications
Exercise is beneficial for people with asthma as it improves lung function, cardiovascular health, and overall fitness. However, patients should be aware of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB), which can cause symptoms such as coughing or shortness of breath during or after exercise.
Pre-exercise Medication: For individuals with EIB, using a quick-relief inhaler before exercise can help prevent symptoms. Long-term management with anti-inflammatory treatments, like ICS, can also reduce the frequency of exercise-induced flare-ups.
5. Importance of Patient Education and Adherence
Effective asthma management goes beyond medication. Educating patients about their condition, proper inhaler techniques, and the development of an asthma action plan are vital components of successful treatment. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers allow for monitoring asthma control, adjusting treatment plans, and ensuring medication adherence.
Personalized Asthma Action Plans: These plans help patients recognize early warning signs of asthma exacerbations and take the appropriate steps, such as using a rescue inhaler or seeking medical attention, to prevent worsening symptoms.
Conclusion
The treatment landscape for asthma has evolved significantly in recent years, with a stronger focus on long-term control, biologic therapies for severe cases, and environmental management. By using a comprehensive approach that includes appropriate medications, lifestyle changes, and patient education, individuals with asthma can manage their symptoms effectively and lead active, fulfilling lives.