ロボアドバイザーで始める資産運用|おすすめ比較と選び方ガイド
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED): Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Effective Treatment Options
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) is an autoimmune condition that affects the muscles and tissues around the eyes, leading to symptoms ranging from mild irritation to severe vision impairment. Closely linked to thyroid disorders such as Graves’ disease, TED can significantly impact eye health, appearance, and quality of life. Recognizing the early signs and seeking timely medical intervention can help prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes.
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) is an autoimmune condition that affects the muscles and tissues around the eyes, leading to symptoms ranging from mild irritation to severe vision impairment. Closely linked to thyroid disorders such as Graves’ disease, TED can significantly impact eye health, appearance, and quality of life. Recognizing the early signs and seeking timely medical intervention can help prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes.
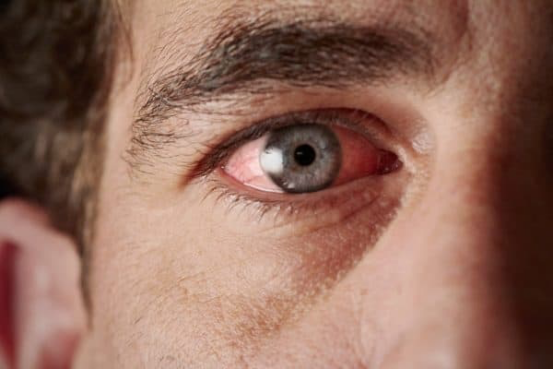
What is Thyroid Eye Disease?
Thyroid Eye Disease, also known as thyroid-associated orbitopathy (TAO) or Graves' orbitopathy, occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the soft tissues and muscles behind the eyes. This leads to inflammation, swelling, and functional impairment of the eyes.
TED is most commonly associated with hyperthyroidism, especially in people with Graves' disease, but it can also develop in individuals with hypothyroidism or normal thyroid function.
Early Symptoms of TED: What to Watch For
The early symptoms of TED can be subtle, making it easy to mistake them for other eye conditions such as dry eye syndrome or allergies. However, persistent or worsening symptoms may indicate the onset of TED.
Common Early Signs:
- Mild swelling around the eyes
- Dryness, irritation, or a gritty sensation
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Excessive tearing or watery eyes
- A sensation of pressure or discomfort behind the eyes
- Slight eyelid retraction, giving the eyes a “staring” appearance
If these symptoms persist or worsen, medical evaluation is recommended to rule out TED.
Progression of TED: More Advanced Symptoms
As TED progresses, symptoms become more pronounced and potentially debilitating. In moderate to severe cases, individuals may experience:
- Bulging or protruding eyes (proptosis)due to swelling of the tissues behind the eyes
- Persistent eyelid swellingand redness
- Difficulty moving the eyes, leading to painful eye movements
- Double vision (diplopia)caused by misalignment of the eyes
- Blurry visionor trouble focusing
In more severe cases, TED can lead to vision-threatening complications that require urgent medical attention.
Serious TED Symptoms That Require Immediate Medical Care
Some TED symptoms indicate severe disease progression and should not be ignored. If you experience any of the following, seek immediate medical help:
- Sudden or worsening double vision
- Severe pain or persistent pressure behind the eyes
- Inability to fully close the eyes, leading to excessive dryness and corneal exposure
- Significant vision loss or changes in color perception
- Loss of peripheral vision
These could indicate optic nerve compression (dysthyroid optic neuropathy, DON), which may lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated.
Risk Factors for Developing TED
Several factors can increase the risk of developing Thyroid Eye Disease, including:
✔ Thyroid Disorders – Most commonly occurs in individuals with Graves' disease, but can also affect people with hypothyroidism.✔ Smoking – One of the most significant risk factors; smokers are at a much higher risk of developing severe TED.
✔ Genetics – A family history of thyroid disorders or autoimmune diseases may increase susceptibility.
✔ Gender and Age – TED is more common in women, particularly between 40 and 60 years old.
✔ Radioactive Iodine Treatment – Some individuals who undergo radioactive iodine therapy for hyperthyroidism may experience worsening TED symptoms.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to reduce their risk or detect TED early.
How is Thyroid Eye Disease Diagnosed?
A comprehensive evaluation by an eye specialist or endocrinologist is crucial for diagnosing TED. The following tests are commonly performed:
1️⃣ Physical Eye Examination – Checking for swelling, eye movement restrictions, and eyelid position.
2️⃣ Thyroid Function Tests – Blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels and antibodies.
3️⃣ Imaging Studies (CT or MRI scans) – Helps assess inflammation, eye muscle involvement, and optic nerve compression.
4️⃣ Visual Field Testing – Determines if TED is affecting peripheral vision.
5️⃣ Ocular Motility Tests – Evaluates the extent of double vision and eye movement restrictions.
Early diagnosis allows for timely treatment, which can prevent vision-threatening complications.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Eye Disease
The treatment approach depends on the severity of TED and whether the disease is in its active (progressive) or inactive (stable) phase.
1. Managing Mild TED Symptoms at Home
For individuals with mild TED, symptoms can often be managed with lifestyle adjustments and eye care:
- Use lubricating eye dropsto relieve dryness and irritation.
- Wear sunglassesto protect against bright light and environmental irritants.
- Elevate your head while sleepingto reduce morning eye swelling.
- Quit smokingto significantly slow disease progression.
2. Medications for Moderate to Severe TED
- Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone)– Reduce inflammation and swelling in the eyes.
- Tepezza (teprotumumab)– FDA-approved therapy that targets inflammation and reduces eye bulging and double vision.
- Radiation Therapy– In some cases, low-dose radiation may help control inflammation in the eye muscles.
3. Surgical Options for Severe TED
For advanced cases, surgery may be required to correct vision problems and relieve pressure in the eye socket:
- Orbital Decompression Surgery– Expands the space around the eyes to reduce bulging and prevent optic nerve compression.
- Strabismus Surgery– Helps correct double vision by realigning the eye muscles.
- Eyelid Surgery– Improves eyelid function to protect the cornea from excessive dryness.
Can TED Be Prevented?
While TED cannot always be completely prevented, taking proactive steps can reduce the risk and severity of symptoms:
✔ Quit Smoking – Smoking significantly increases the risk and severity of TED.
✔ Control Thyroid Levels – Regular thyroid check-ups and proper medication management can help stabilize the condition.
✔ Protect Your Eyes – Wear sunglasses, use artificial tears, and avoid excessive screen time.
✔ Monitor for Early Symptoms – If you have a thyroid disorder, be vigilant about any changes in eye appearance, comfort, or vision.
Final Thoughts: Early Recognition and Treatment Matter
Thyroid Eye Disease can have a major impact on vision and quality of life, but early detection and intervention can make a significant difference. If you notice persistent eye discomfort, swelling, or vision changes, it’s essential to consult an eye specialist as soon as possible.
With proper medical care, lifestyle changes, and advanced treatment options, TED can be effectively managed, ensuring better eye health and long-term well-being.











