倉庫内作業 正社員の求人をお探しの方へ|安定して働ける物流現場の仕事
Why Seniors Should Pay Attention to These Atopic Dermatitis Signs
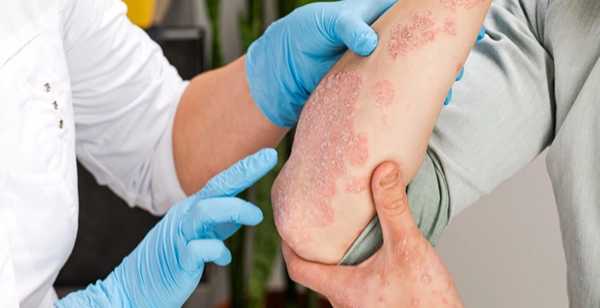
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that affects individuals of all ages. While it’s often associated with children, seniors are not immune to it.
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that affects individuals of all ages. While it’s often associated with children, seniors are not immune to it.
For older adults, ignoring the signs of atopic dermatitis can lead to worsening symptoms, infections, and a decrease in overall quality of life. Below are key signs that seniors should look out for and why they shouldn’t be ignored.
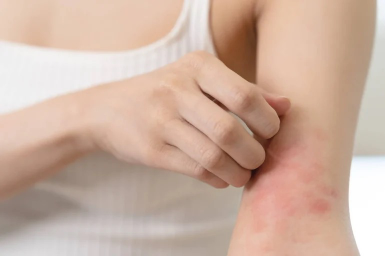
1. Dry, Itchy Skin
Dry, itchy skin is a hallmark symptom of atopic dermatitis. As we age, our skin naturally becomes drier, but when itching becomes persistent or intense, it could indicate eczema. Seniors may notice this issue on their arms, legs, or other areas of their body. Dry and itchy skin can interfere with sleep and daily activities, making it vital to seek treatment early. Left untreated, the itching can become worse, potentially leading to open sores from scratching.
2. Red, Inflamed Patches
Red, inflamed patches of skin, particularly in the folds of the skin such as the elbows or behind the knees, are another sign of atopic dermatitis. These patches may be tender to the touch, swollen, or even weep fluid in severe cases. For seniors, these inflamed patches can be painful and lead to secondary infections. Ignoring these symptoms can allow the condition to worsen, potentially causing chronic irritation and discomfort. Early intervention can help reduce inflammation and prevent infections.
3. Skin Thickening
As atopic dermatitis persists over time, seniors might notice their skin becoming thickened or leathery in certain areas. This condition, called lichenification, occurs when the skin reacts to constant scratching or irritation. It can cause the skin to become rough, dry, and tough. Lichenification is a sign that the eczema has become more chronic, and if not treated, it may become difficult to reverse. Managing the condition early can help reduce thickening and keep the skin smooth.
4. Crusting or Flaking
Seniors with atopic dermatitis may experience the formation of crusts or flakes on their skin, particularly during flare-ups. This can be frustrating and embarrassing, especially when the flaking occurs on visible areas like the face, neck, or hands. Crusting or flaking skin not only affects appearance but can also cause discomfort. These symptoms should not be ignored, as they can lead to further skin breakdown and an increased risk of infection. Proper skincare and treatment can help minimize these issues.
5. Changes in Skin Color
Long-term atopic dermatitis can lead to changes in skin pigmentation, leaving areas of the skin darker or lighter than the surrounding tissue. These changes, known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, can be especially concerning for seniors who value maintaining healthy, youthful-looking skin. Once these color changes occur, they can be difficult to reverse. By managing eczema early on, seniors can reduce the risk of permanent skin discoloration and maintain more even skin tone.
6. Increased Sensitivity to Triggers
Seniors with atopic dermatitis often develop increased skin sensitivity. This means that their skin may react more strongly to common irritants such as certain fabrics, soaps, perfumes, or even changes in the weather. This heightened sensitivity can cause flare-ups, which further aggravate the condition. Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as using hypoallergenic products or choosing gentle fabrics, is crucial in managing atopic dermatitis and reducing skin irritation.
7. Infections from Scratching
Atopic dermatitis can lead to broken skin due to excessive scratching. Seniors who scratch the affected areas may risk introducing bacteria into the skin, resulting in infections. Common infections associated with eczema include bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. If seniors notice signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, swelling, or pus, they should seek medical attention immediately. Treating eczema early can prevent the skin from becoming broken and reduce the risk of infection.
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis may be more commonly thought of as a childhood condition, but seniors should also be vigilant about recognizing its signs. Dry, itchy skin, red patches, thickened skin, crusting, and increased sensitivity are all symptoms that should not be ignored. Seniors who experience these signs should seek treatment promptly to prevent complications and improve their skin health. By maintaining a proper skincare routine, avoiding triggers, and consulting a healthcare provider, seniors can manage eczema effectively and ensure they continue to enjoy a comfortable and healthy life.